Brief overview of the critical roles of campaigns and ad groups in Google Ads
In Google Ads, campaigns and ad groups play distinct yet interconnected roles in shaping successful advertising strategies. Campaigns act as the overarching structure where goals, budgets, and broad targeting are defined. Within these campaigns, ad groups allow for a more detailed focus, targeting specific sets of keywords and tailored ad creatives to closely match user intent. This hierarchical setup ensures both high-level strategic control and fine-grained targeting, essential for optimizing ad performance and achieving campaign objectives efficiently.
Decoding Campaigns in Google Ads
Defining a Campaign in Google Ads
A campaign in Google Ads is a set of ad groups (ads, keywords, and bids) that share a budget, targeting settings, and other settings. It is designed to achieve a specific marketing goal, such as driving website traffic or increasing product sales. Campaigns are categorized by their advertising networks, such as the Search Network, Display Network, and YouTube, and are tailored based on the type of customer actions you want to drive.
Key Objectives and Settings of Campaigns
The objectives of campaigns in Google Ads can vary widely, depending on the desired outcome. These objectives include increasing brand awareness, generating leads, driving traffic to a website, or boosting sales. Key settings in a campaign encompass the choice of network, target audience demographics, geographical targeting, budgeting, and bidding strategies. Each setting plays a crucial role in how the campaign reaches potential customers and how effectively it spends its budget.
Table 1: Overview of Campaign Settings and Options
| Setting Category | Description | Options |
| Type | Determines the platform where ads will appear. | Search, Display, Video, Shopping, App, Performance Max |
| Budget | Sets the amount of money allocated for the campaign. | Daily budget, total budget |
| Bidding Strategy | Method used to bid for ad placement. | Cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-mille (CPM), cost-per-engagement (CPE), etc. |
| Targeting | Defines who will see the ads. | Location, language, age, gender, device, audience interests |
| Ad Scheduling | Controls when ads will be shown. | Specific days of the week, times of day |
| Ad Extensions | Additional information to enhance ads. | Sitelinks, callouts, structured snippets |
This table provides a snapshot of key campaign settings in Google Ads, offering a clear understanding of the various options available for tailoring campaigns to meet specific advertising objectives.
Exploring Ad Groups and Their Functionality
What Constitutes an Ad Group?
An ad group in Google Ads is a collection of one or more ads that share similar targets. Each ad group contains ads that are targeted to a specific set of keywords and are designed to be shown to users based on those keyword searches. Essentially, ad groups allow for more detailed and specific targeting within a campaign. They enable advertisers to group their ads by common themes, products, or services, and tailor the ads and keywords in each ad group to align closely with a specific aspect of their overall campaign goal.
Role of Ad Groups in a Google Ads Campaign
Ad groups play a critical role in the structure and success of a Google Ads campaign. They provide the means to organize ads by theme or product, which allows for more precise targeting and messaging. This organization ensures that the ads displayed are as relevant as possible to the user’s search query or interest, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion. In a well-structured Google Ads campaign, each ad group targets a specific area of the campaign’s overall objective, contributing to more effective and efficient ad performance.
Core Functions and Features of Ad Groups
- Targeted Keyword Grouping: Ad groups allow for the clustering of similar keywords, enabling ads to be more targeted and relevant to user searches.
- Customized Ad Copies: Within each ad group, ads can be specifically tailored to match the group’s theme or targeted keywords, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
- Bidding Control: Ad groups provide the ability to set bids for specific keywords or placements, giving more control over how much you spend on different aspects of your campaign.
- Performance Tracking: Ad groups offer detailed performance metrics, allowing advertisers to analyze and optimize the effectiveness of different themes or product groupings within their campaigns.
- Testing Opportunities: They are ideal for A/B testing different ad variations, helping to determine the most effective ad copy, calls to action, and keyword combinations.
- Flexibility in Modifications: Ad groups offer the flexibility to easily modify or switch out ads, keywords, and bids without affecting the overall campaign structure.
Campaigns vs. Ad Groups: A Comparative Analysis
Differences in Purpose and Structure
Campaigns and ad groups within Google Ads serve distinct but complementary purposes in your digital marketing strategy. A campaign is the broader structure, setting the stage for your overall advertising objectives, budget, and targeting settings. It’s where the big-picture decisions are made, and broad strategies are set. On the other hand, ad groups function under the umbrella of campaigns and offer a more granular level of management. They allow for the detailed organization of ads, tailored to specific segments of your target audience, and focused on narrower objectives that align with the broader campaign goals.
Table 2: Side-by-Side Comparison of Campaigns and Ad Groups
| Feature | Campaigns | Ad Groups |
| Purpose | Set overall advertising objectives and manage budget. | Focus on specific sets of keywords and ads for targeted messaging. |
| Structure | Higher-level, broader scope. | More detailed and specific within the campaign. |
| Targeting | Broad targeting options (geographical, demographic, etc.). | Specific targeting based on keywords, ad placements, and audience segments. |
| Budget Management | Overall budget set for the entire campaign. | Budget spent is controlled by campaign settings, but bids can be managed at the ad group level. |
| Ad Variations | Not specific to campaigns. | Allows for testing multiple ad variations targeting different keywords or demographics within the same campaign. |
| Reporting | High-level performance metrics for the campaign. | Detailed performance metrics for each set of ads and keywords. |
Strategic Use of Campaigns and Ad Groups in Marketing Efforts
Understanding the strategic use of campaigns and ad groups is key to maximizing the effectiveness of your Google Ads. Campaigns should be used to define your broad marketing goals and allocate resources effectively, while ad groups should be focused on refining and targeting your message to specific audience segments or interests. This dual-level approach allows for both comprehensive planning and detailed execution, making your advertising efforts both broad-reaching and precisely targeted.
Fig 1: Flowchart Showing Decision Process for Campaign and Ad Group Creation
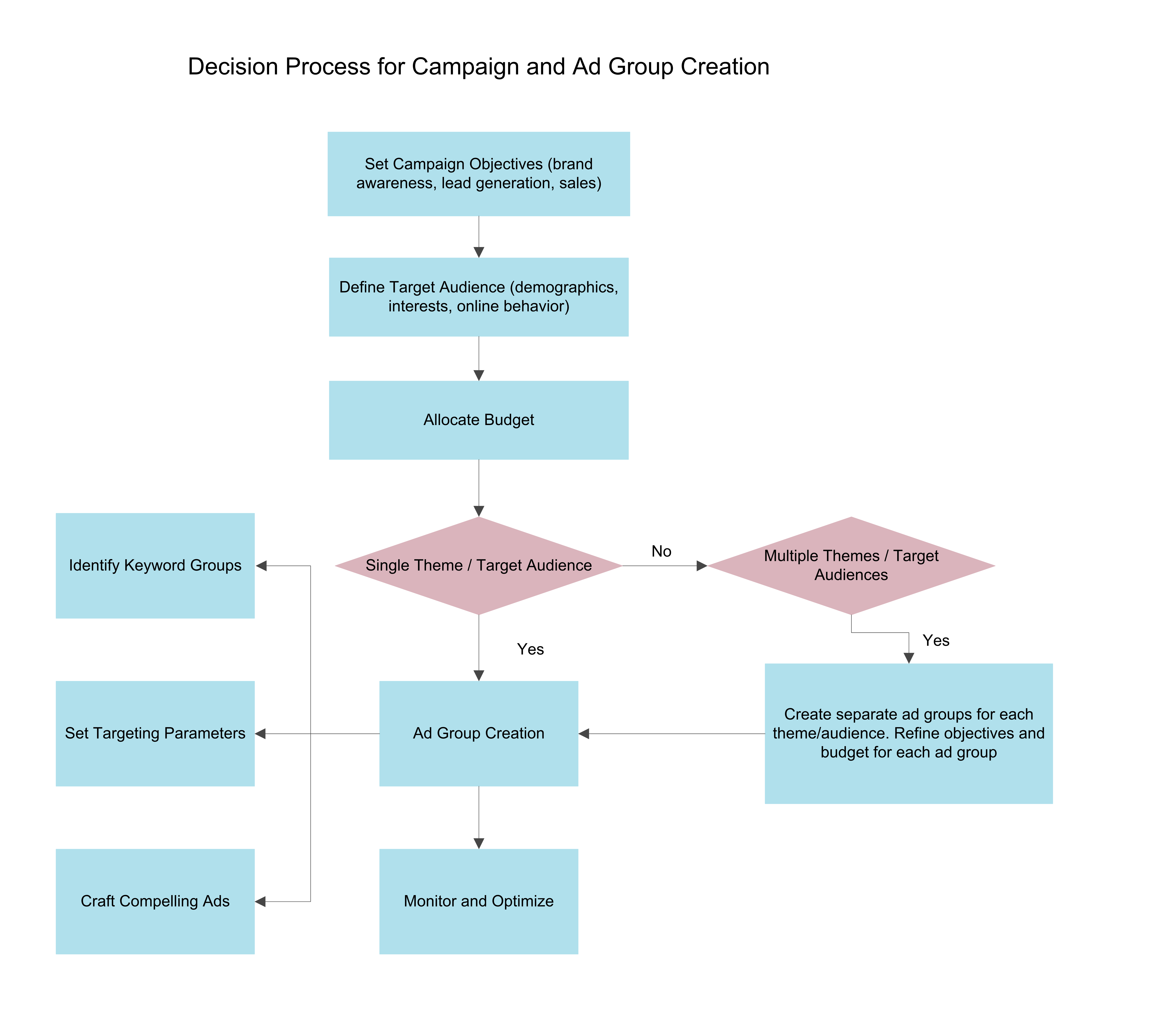
Timing of Ad Group Creation
When to Create Ad Groups: Before, After, or During Campaign Setup
Deciding when to create ad groups within your Google Ads campaign setup is a strategic choice that can impact the effectiveness of your advertising efforts. Typically, ad groups can be created before launching the campaign to ensure a structured start, during the campaign setup for a more integrated approach, or even after the campaign has begun for added flexibility and response to performance data.
Pros and Cons of Each Timing Option
- Before Campaign Launch:
- Pros: Allows for thorough planning and a structured approach. Ensures that campaigns start with a detailed targeting strategy.
- Cons: May lack real-time data to inform targeting and ad variation decisions.
- During Campaign Setup:
- Pros: Integrates ad group creation with campaign planning, allowing for a cohesive strategy. Utilizes initial campaign data for informed decisions.
- Cons: Can be time-consuming and may delay campaign launch.
- After Campaign Launch:
- Pros: Enables responsiveness to real-time performance data. Allows for adjustments based on actual campaign insights.
- Cons: Might lead to initial inefficiencies in campaign targeting and budget allocation.
Best Practices for Effective Ad Group Timing
Effective ad group timing involves balancing preparation with flexibility. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of your campaign goals and target audience before creating ad groups. However, be prepared to adjust and create new ad groups as you gather performance data and insights. Regularly review and refine your ad groups based on campaign performance, audience behavior, and changing market trends. This dynamic approach ensures that your ad groups remain relevant and effective throughout the campaign lifecycle.
Practical Scenarios and Examples
Case Studies Demonstrating Campaign and Ad Group Usage
To illustrate the effective use of campaigns and ad groups in Google Ads, let’s explore a couple of case studies that demonstrate how businesses have successfully utilized these tools to achieve their advertising objectives.
Case Study 1: E-commerce Retailer
- Scenario: An online retailer specializing in eco-friendly products wanted to increase sales while also raising brand awareness.
- Campaign Strategy: They set up separate campaigns for brand awareness (using Display ads) and for driving sales (using Shopping ads).
- Ad Group Tactics: Within the sales campaign, they created specific ad groups for each product category, such as ‘organic skincare’ and ‘sustainable home goods.’ Each ad group targeted keywords relevant to its products.
- Outcome: This structured approach allowed for tailored ad messaging and bidding strategies, leading to a 30% increase in conversion rate for product sales and a significant boost in brand recognition.
Case Study 2: Local Service Provider
- Scenario: A local plumbing service aimed to attract more emergency repair jobs in their city.
- Campaign Strategy: The service provider set up a Search campaign targeting their city.
- Ad Group Tactics: Within this campaign, they created different ad groups based on services, such as ‘leak repairs’ and ‘pipe installations,’ each with specific keywords and localized ad copy.
- Outcome: By using distinct ad groups, they were able to match customer queries more accurately, resulting in a 40% increase in emergency service calls.
These case studies showcase how different types of businesses can effectively use campaigns and ad groups in Google Ads to meet their unique marketing goals. By thoughtfully structuring campaigns and ad groups, businesses can ensure that their ads are targeted, relevant, and successful in driving desired outcomes.
Conclusion
Campaigns and ad groups work together in a symbiotic relationship within Google Ads. While campaigns set the overarching strategy and goals, ad groups provide the necessary granularity to target specific audience segments and keywords more precisely. This two-tiered structure allows for a comprehensive and nuanced approach to digital advertising, ensuring that every ad reaches the right audience with the right message.
In terms of timing and structuring ad groups, the key is to balance strategic planning with flexibility. Creating ad groups can be most effective when done in tandem with campaign setup, allowing for a cohesive strategy from the outset. However, it’s also crucial to remain adaptable, ready to create new ad groups or adjust existing ones based on real-time data and performance metrics. This approach ensures that your campaigns are not only well-organized from the start but also continue to evolve and improve over time.


No responses yet